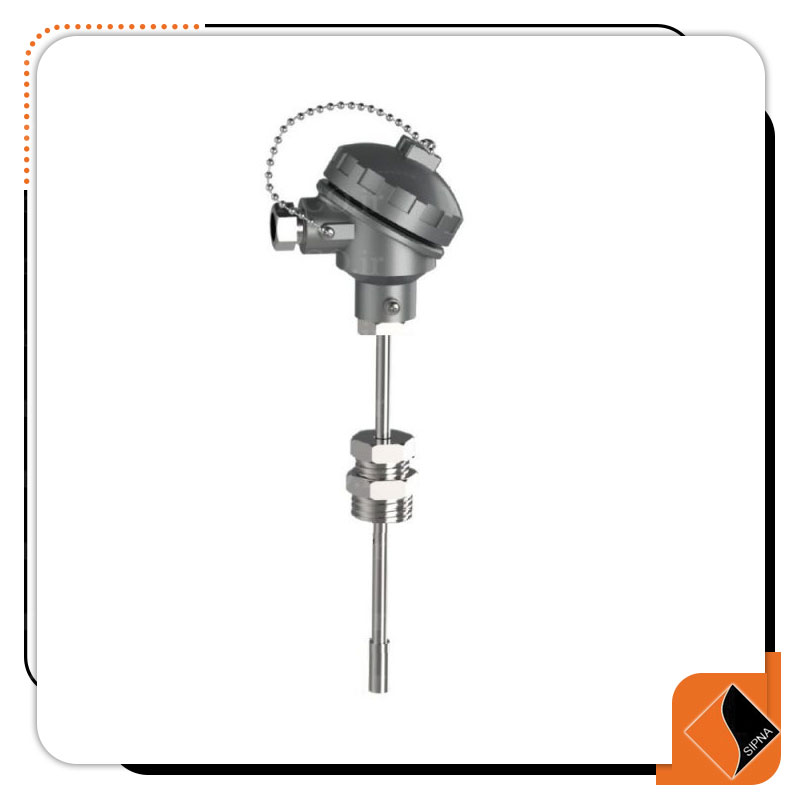
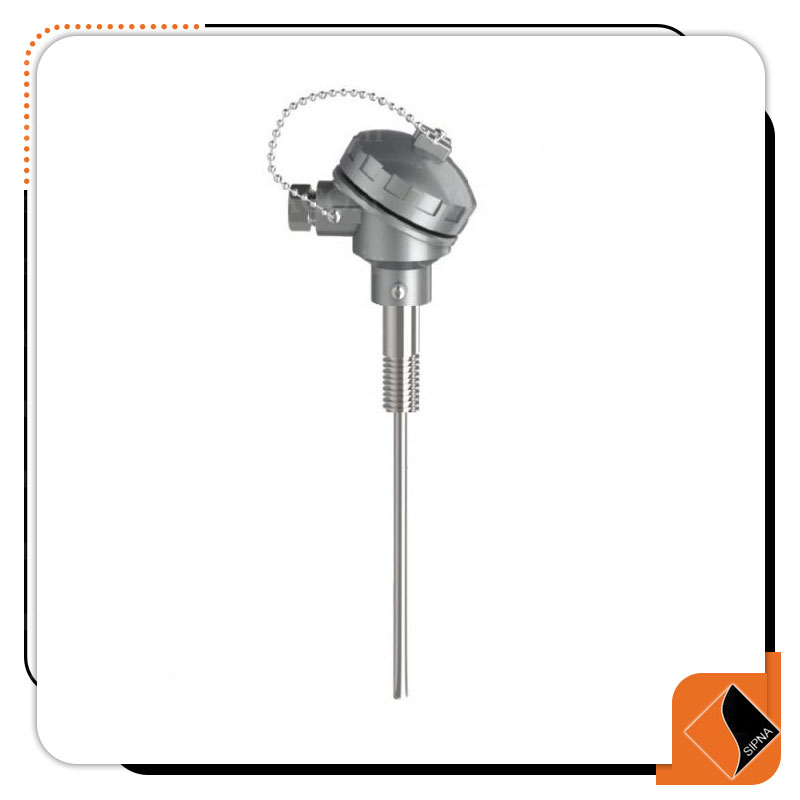
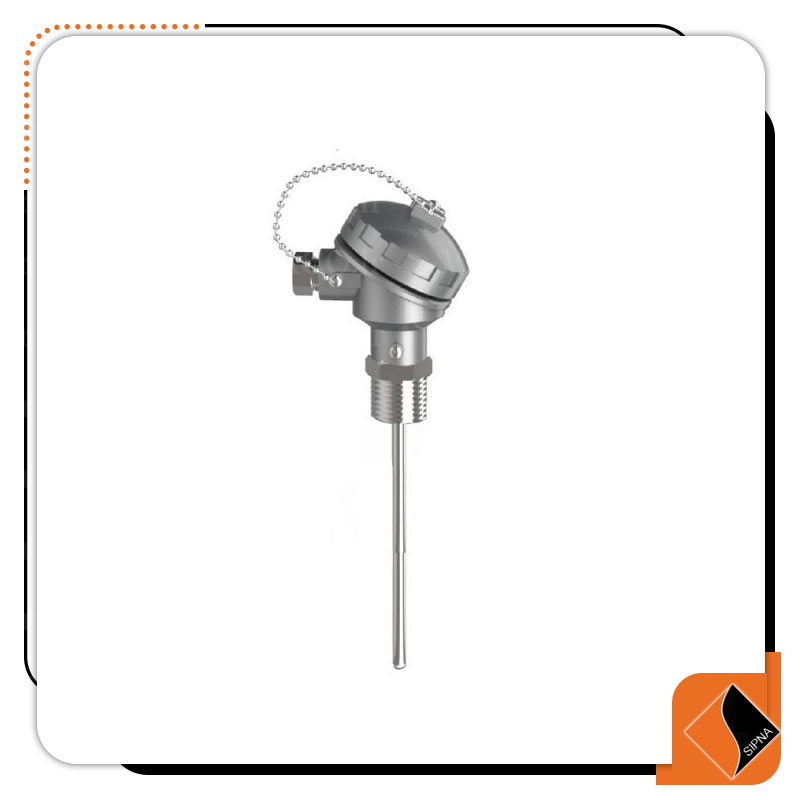
R-103 Series RTD with movable head and thread
R-103 Series RTD with movable head and thread
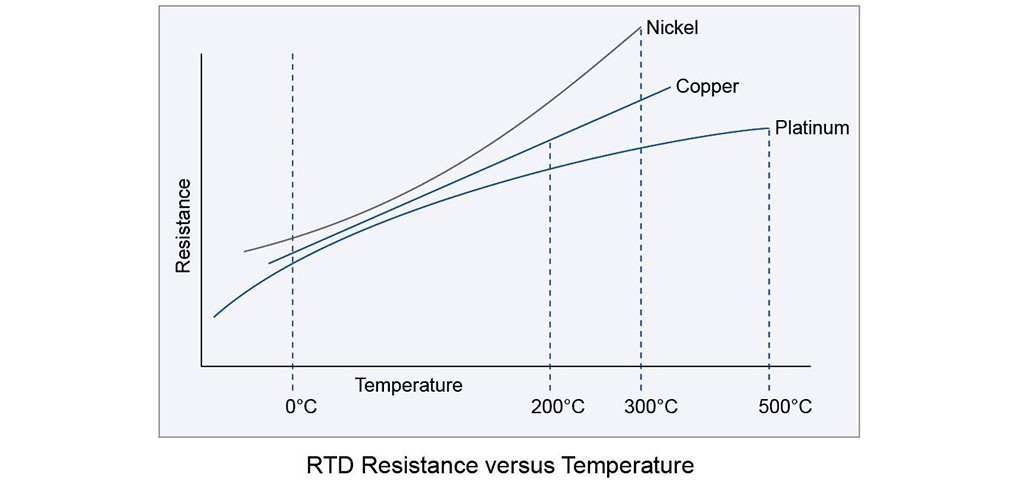
RTDs are temperature sensors that use the resistance / temperature ratio of materials to measure temperature. RTDs have higher accuracy and stability than thermocouples, which are usually in the range below 600 ° C. Resistance temperature sensors are generally made of copper, nickel or platinum, which show a certain resistance at a certain temperature. RTD is an ideal solution if we want to measure temperature with high accuracy, because it has good linear properties over a wide range of temperatures. RTD does not generate output on its own. External electronic devices are used to measure the resistance of a sensor by passing a small current through the sensor to generate voltage. Normally 1 mA or less current flows through them and the voltage across the sensor is measured by the device.
Typical RTD means that the section that measures temperature has a larger diameter and is used at times when the tip
The RTD must withstand higher temperatures, or the chamber inside which the sensor is placed is designed with this structure in mind.
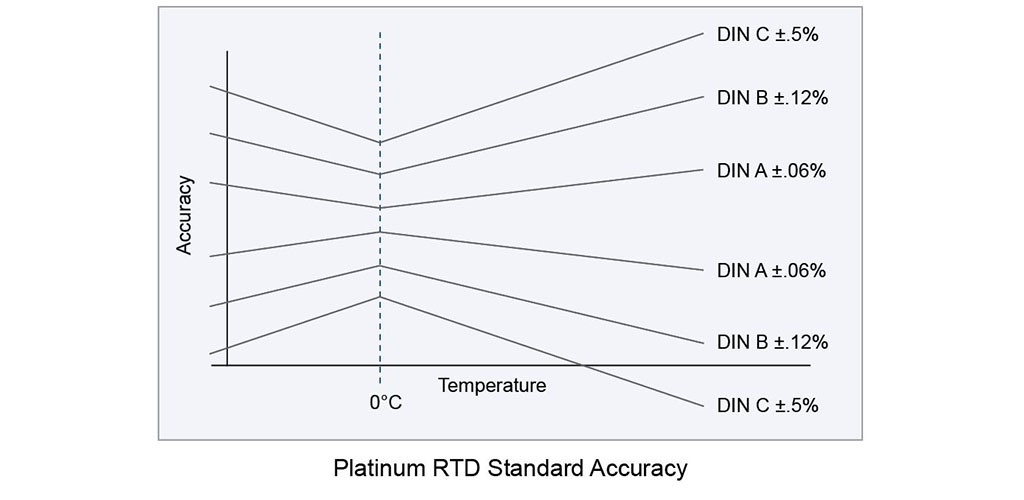
RTDs are made with several standard and bearing curves. The most common standard curve is the ‘DIN’ curve. This curve describes the temperature resistance characteristics of a platinum, 100 ohm sensor, standard tolerances and measurable temperature range.
There are three standard tolerance classes for DIN RTD. These tolerances are defined as follows:
A: ± (0.15 + .002 | T | ° C)
B: ± (0.3 + .005 | T | ° C)
C: ± (1.2 + .005 | T | ° C)
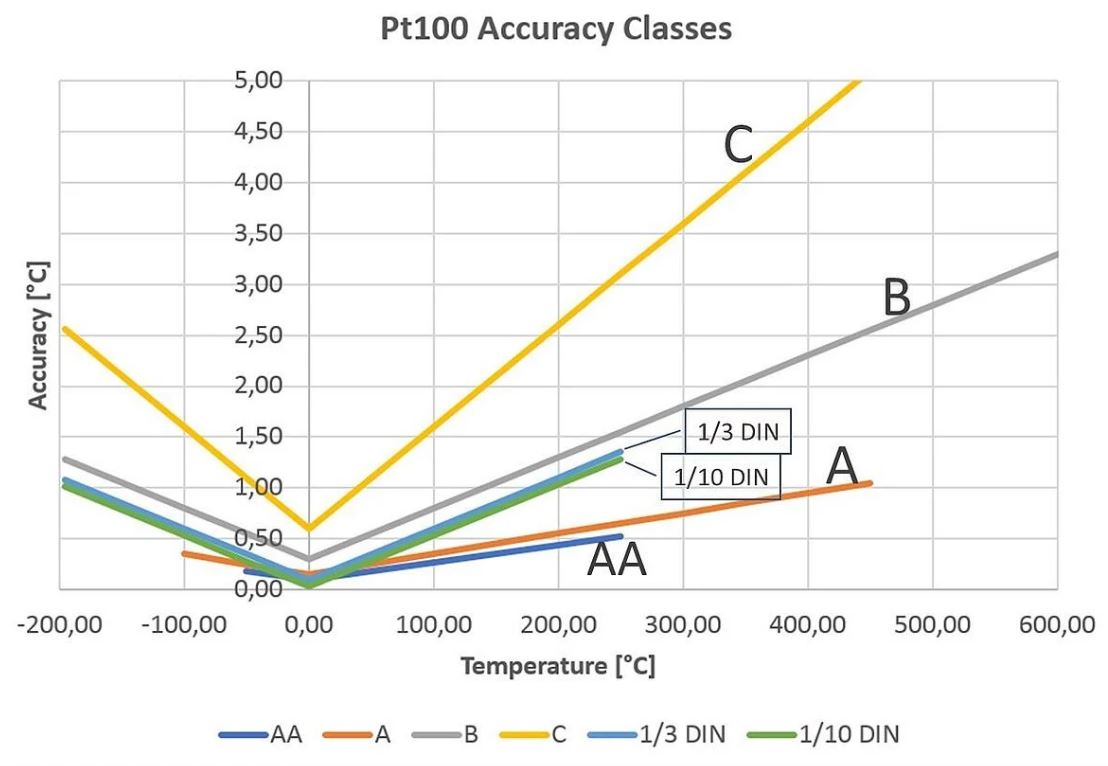
The following curves show the types of RTDs and the ratio of output resistance to temperature tolerance:
RTD sensors are divided into three general types in terms of the number of output wires:
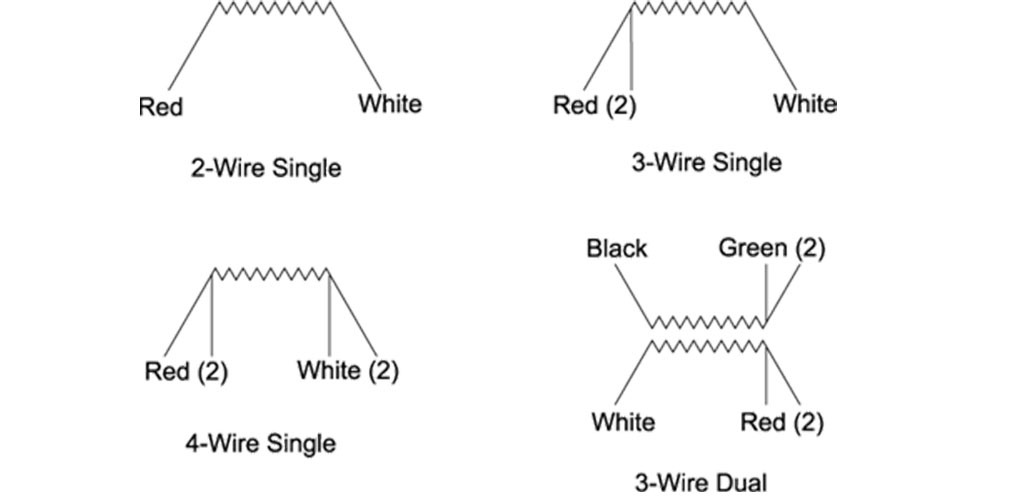
Two wires are commonly used in applications where accuracy is not important. Two-wire configuration makes the simplest measurement technique possible, but suffers from an inherent inaccuracy due to the resistance of the sensor wires. In two-wire configuration, there is no way to directly compensate for the resistance of the wire, which increases the compensation of the resistance measurement.
Three-wire sensors are made with a compensation loop to increase measurement accuracy. With these settings, the controller / measuring device performs two measurements. The first measurement measures the overall resistance of the sensor and the connecting wires. The second measurement is the resistance of the compensation ring. By subtracting the compensation ring resistance from the total resistance, a net resistance is calculated. The three-wire sensors provide the most common combination in terms of accuracy and comfort.
In four-wire sensors, resistance measurements are measured with great accuracy, and this method gives the best accuracy, many industrial controllers / measuring devices can not measure real four-wire.
RTD with the head or the head means that the terminal connections are placed inside an aluminum box on top of the thermocouple and the head is selected according to the environmental conditions. The heads are divided into two general parts IP67 head Which has a degree of protection against dust and condensate, which is used in most cases, and later explosion-proof heads, called Explosion Proof, which are widely used in the oil industry.
Movable thread means that the thread is not welded to the sheath and wherever the sheath is needed, it is fixed by a wrench. The price of all products offered in this category is based on the 1/2 inch NPT / BSP moving thread which is more used in industry. If you need to change the thread, be sure to mention this important in the description section when buying.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.